Hello there, In this article, we'll take a look at some of the basic commands used in Linux-based systems.
Anatomy of a basic Linux prompt
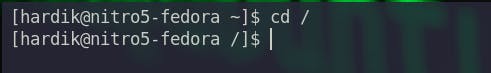
- In lines 1 and 2, we see
hardik@nitro5-fedora. Herehardikis the username of the logged-in user andnitro5-fedorais the name of the pc. - In line 1,
~indicates that we are in the home directory. - In line 2,
/indicates that we are at the root of the filesystem. - The
$symbol indicates that you are interacting with the system as a regular user. If you have sudo privileges, the$turns into a#.
NOTE: From here on now, I’ll be using zsh instead of bash. But don't go away just yet. The commands discussed here work just the same on bash as well. :P
Some basic Linux commands
date
date command is used to show the current system date and time.

ls
ls command lists the files present in the current directory.
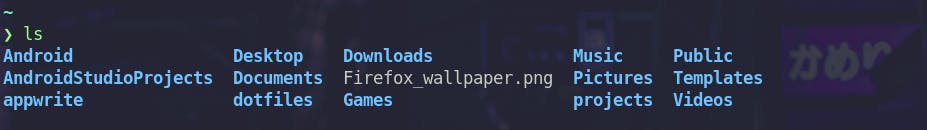
Let’s take a look at some important flags for ls command
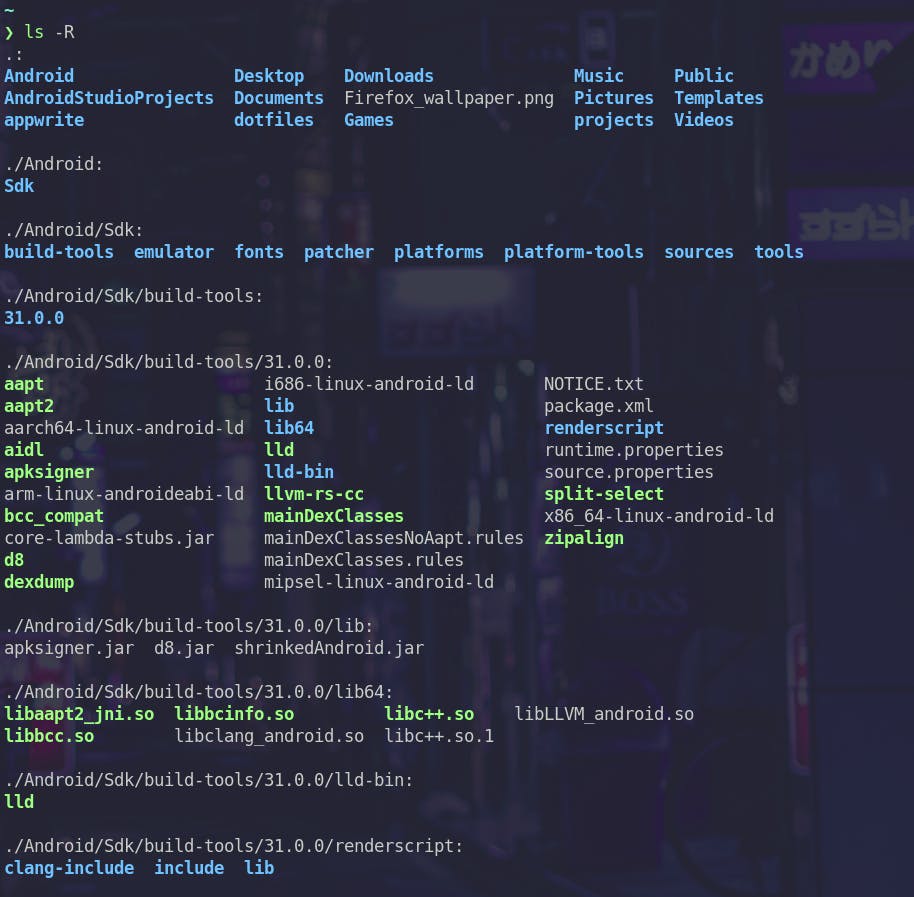
-RThis flag lists the files recursively i.e. it will also list the file present in subdirectories and their subdirectories and so on
Here’s a sample
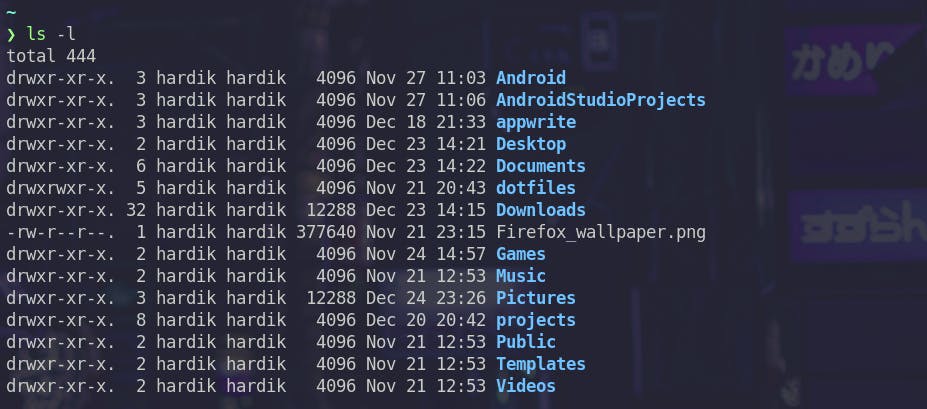
-lThis flag shows some additional information about the files like permission string, owner, group of the owner, file size in bytes
-aThis flag lists hidden files as well
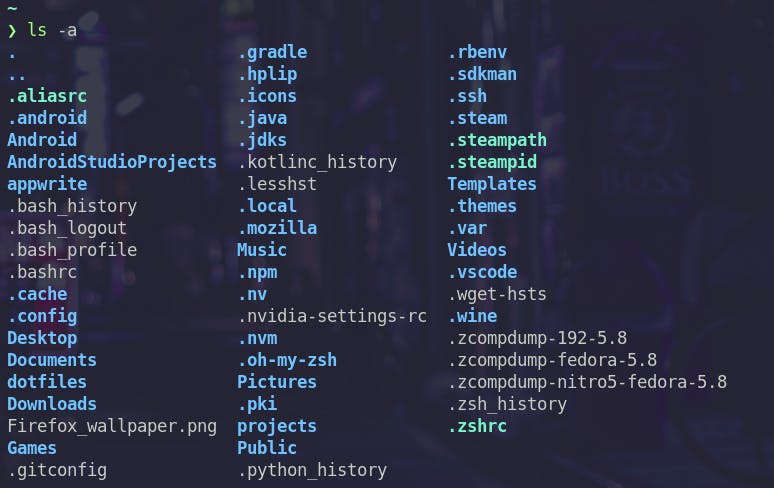
cat
cat command is used to display, copy, combine and create new files.
Creating new files
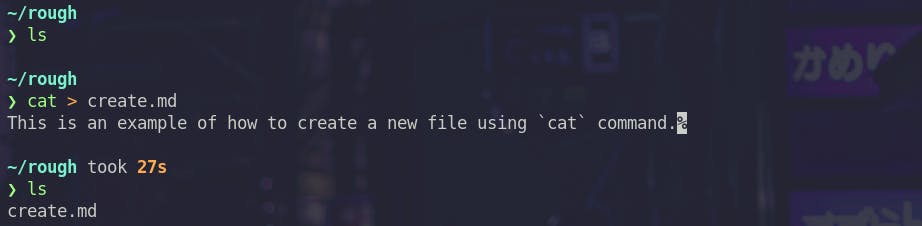
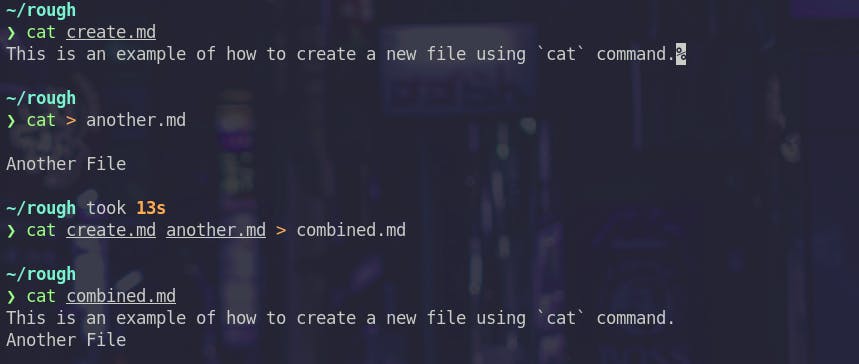
Viewing a file

Combining two files
pwd
pwd stands for print working directory and does the same.

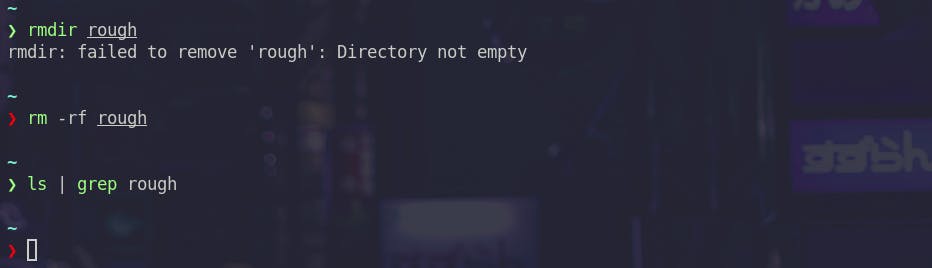
rm
rm is used to delete files. rmdir can be used to delete directories.
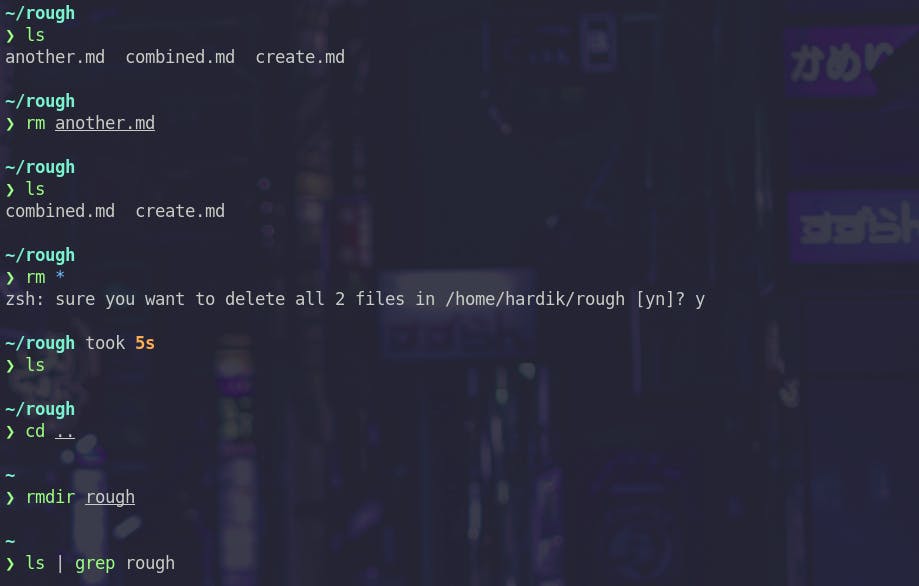
You can use -rf flag to delete a directory recursively.
cd
cd stands for change directory and is used to do the same.
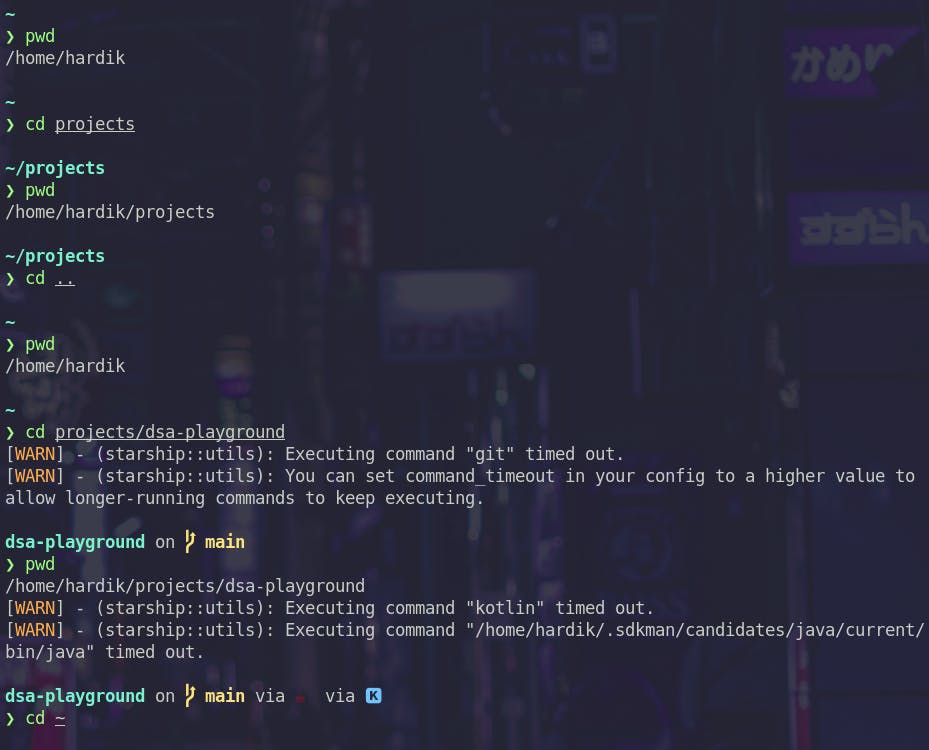
Please ignore the warnings. They are related to my prompt configuration.
Some important cd commands
cd ..is used to navigate to one level up in file system.cd ~navigates you to your home folder.
mkdir
mkdir is used to create a new directory.

mv
mv stands for move. It is used to move files around the file system. It can also be used to rename files
SYNTAX
mv [OPTIONS] source destination

cp
cp stands for copy and is used to copy files and folders
SYNTAX
cp [OPTIONS] source destination

man
man command is used to access documentation of the commands that are available in the os. Here is a sample
man curl
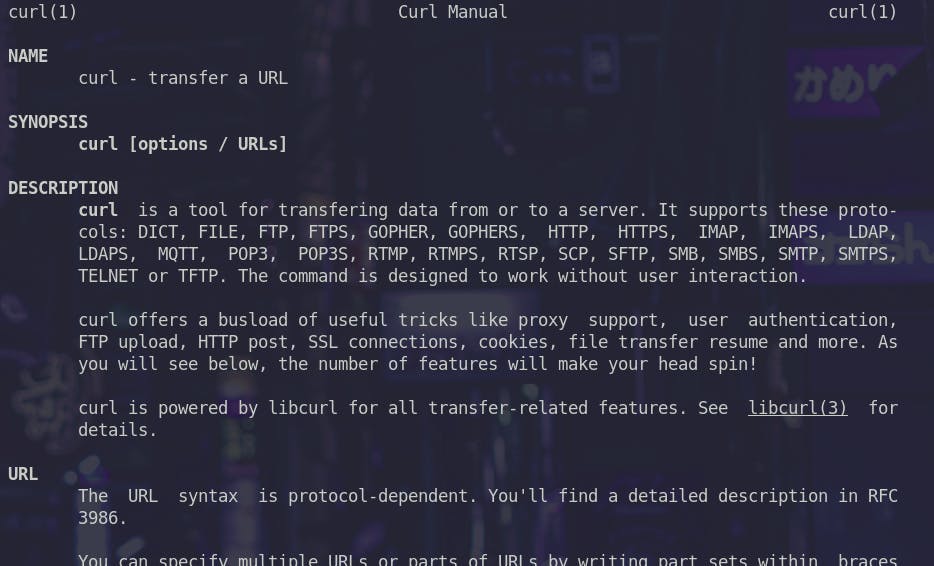
To exit this page, press q
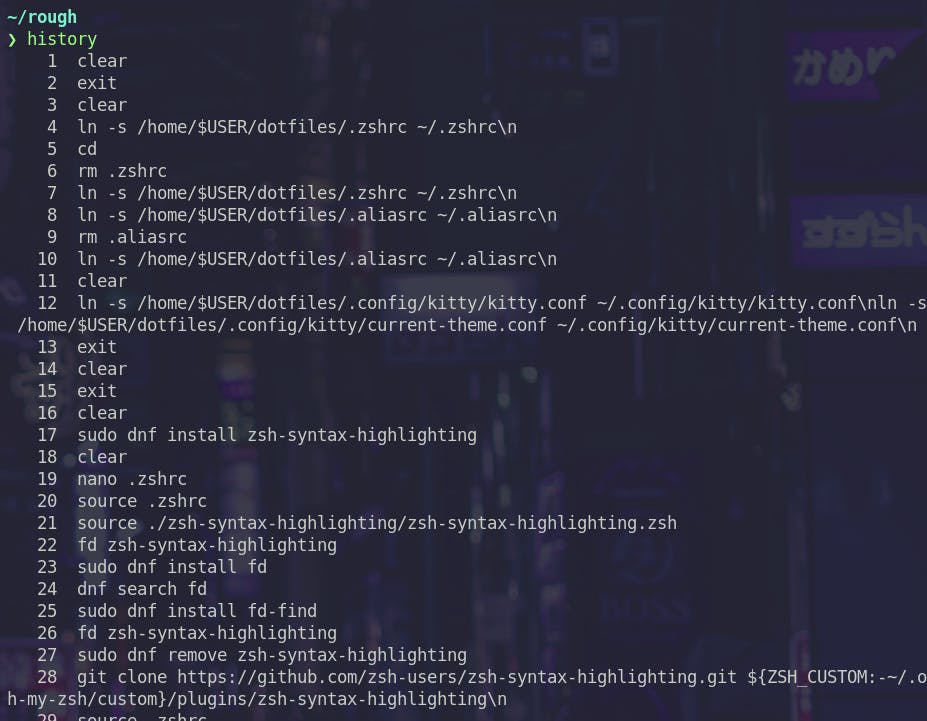
history
history command shows the commands used in this terminal session.
clear
clear command clears the terminal. In modern terminal emulators, you can press Ctrl + L to do the same.
Hope you liked this short article. See you next time. :D

